

Tungsten carbide(WC) is one of the hardest carbon-based compounds. In its applications, we can find it used to make cutting tools, jewelry, abrasives, weapons, surgical instruments or special coatings for various high-demand parts.
Resin diamond grinding wheel and vitrified diamond grinding wheel is uaually used for thermal spray coating grinding, and Moresuperhard can also provide diamond sanding belt for polishing tungsten carbide coating, ceramic coating,etc...

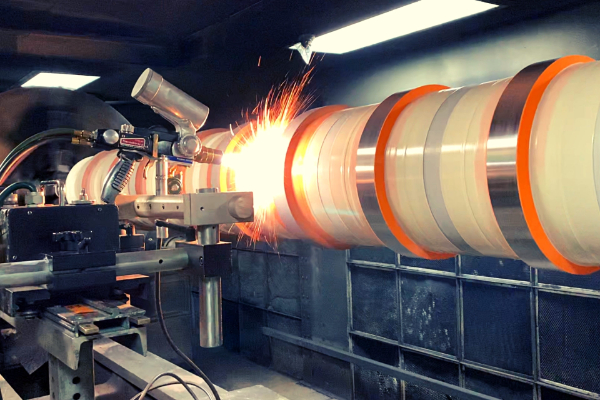
Tungsten carbide coating is a coating that uses supersonic flame spraying, explosion spraying or plasma spraying to heat powder containing tungsten carbide hard particles and soft metals such as cobalt, nickel, chromium, etc. to a
molten or semi-molten state, and then hits the surface of the substrate material at a very high speed to flatten the powder particles and adhere to the surface of the substrate material. The coating has good impact resistance and toughness, and has high bonding strength and good density with the substrate. It has high wear resistance. The surface hardness is generally above 1000HV0.3, which can effectively improve the wear resistance of the surface of the parts. Therefore, it is widely used in machinery, aviation, aerospace and other fields. Metallographic testing is n important means to evaluate the quality of coatings. Through metallographic testing, the organizational structure of the coating, such as pores, oxides, cracks, foreign contaminants, etc., can be directly observed. However, since tungsten carbide coating is a composite coating, containing hard and brittle phases and bonding phases, and the coating contains a certain amount of pores, the hardness distribution of the coating is extremely uneven, making the thermal spray coating extremely sensitive to metallographic preparation technology. The metallographic preparation process may cause coating defects such as delamination, transverse cracks, and interface separation in the coating microstructure. In addition, the porosity of the coating will increase or decrease significantly due to inappropriate metallographic preparation technology, thereby affecting the evaluation results of the tungsten carbide coating structure.
As one of the hardest materials, according to the Mohs hardness, the hardness of tungsten carbide is between 8.5 and 9.5, which is only surpassed by very few materials such as diamond. This material is born from the combination of carbon and tungsten, doped with a small amount of cobalt, and sintered to form one of the so-called CERMET (CERamic METal), which is considered to be one of the most durable and durable compounds in the industry.
The composite layer can effectively improve the surface quality of parts, reduce maintenance costs and extend service life, so it is widely used in the improvement of surface performance of parts in the fields of petrochemical, engineering machinery, navigation, etc.
Tungsten carbide materials have good thermal stability, chemical stability, oxidation resistance, high melting point, high hardness and good wear resistance, so they are often used as surface coatings. However, pure tungsten carbide has poor wettability and cannot be directly used for coating preparation. Therefore, metals such as Co and Ni are often used as bonding metals and mixed with pure tungsten carbide powder to make cemented carbide and wear-resistant coatings.
Supersonic flame spraying

Supersonic flame spraying technology, also known as high-speed oxygen-fuel flame (HVOF) (spraying) technology, is a technology based on high-speed particles to obtain coatings. Using a special combustion chamber or a special nozzle, the gas or liquid fuel is sprayed to form a high-speed, high-pressure, high-temperature combustion flame flow. The metal powder is sent into the flame flow for heating by an inert gas. The molten metal powder is accelerated to hit the substrate surface and solidify quickly, and is continuously deposited to form a coating.
Characteristics and properties of tungsten carbide
Tungsten carbide is a very versatile material that can be alloyed to obtain a wide range of properties. Its extraordinary hardness can be used to shape and cut almost any other material, and its resistance to high temperatures allows it to work at high speeds, maximizing its value as a cutting tool.
For this reason, it is increasingly used to work, in addition to the typical materials of very high hardness, in various steel alloys, from the most conventional and, due to their properties, the most corrosion-resistant. For example manganese steel or tool steel.
Another application for the use of tungsten carbide, due to its reduced ductility and high mechanical resistance, is in the coating of parts that are subject to continuous friction and must have a high wear resistance, such as bearings or rotating elements, where it is applied in the form of coatings using thermal projection systems such as HVOF.
 The most relevant properties of tungsten carbide:
The most relevant properties of tungsten carbide:
* Extremely high hardness.
* Low ductility.
* High mechanical resistance.
* Wear resistance.
* Heat resistance, maintaining its hardness at temperatures above 500°C.
* Corrosion resistance.
How to grind tungsten carbide coating?
Although tungsten carbide coating is often used to make tool tips, especially cutting tools, it also needs to be ground because it must meet certain specifications to give the workpiece used with the necessary shape and finish.
This process can only be carried out by abrasive methods. According to its hardness, the appropriate abrasive that can work effectively is diamond-based abrasive.

Currently, cemented carbide is mainly processed with resin bond diamond grinding wheel. Ceramic bond diamond grinding wheel is used for rough grinding, and the grit size can be selected from 120#, 150# or 200#; resin bond diamond grinding wheel can be selected for fine grinding, and the grit size can be selected from 250#, 300# or 400#. This solution can improve grinding efficiency by 2 to 3 times, save time and cost, and bring more benefits to the enterprise.
Grinding is to use a high-speed rotating diamond grinding wheel to make the surface roughness of the processed parts reach Ra0.4~Ra0.6μm through rough grinding and fine grinding, and the surface roughness can reach Ra0.1~Ra0.2μm after polishing.
Due to the friction between the workpiece and the grinding material, these processes may generate very high temperatures, so it is recommended to perform this grinding, paying special attention to its grinding heat effect, which can be prevented by adding coolant or properly adjusting the cutting and feed speeds and exposure time to prevent the material from getting too high a temperature that may damage it.
The most effective way to remove materials such as tungsten carbide or any other high hardness coating is diamond belt grinding.
As for the particle size selection, it will depend on the amount of material that needs to be extracted and the necessary finish. In major roughing processes, such as honing cylinders to remove and repair coatings, coarse-grit diamond belts (357µm/P40 or 251µm/P60) can be used.
If polishing or low roughness is required, fine-grit diamond belts (46µm/P320 or 30µm/P500) can be used, which can achieve Ra roughnesses of about 0.1µm depending on the process.
For critical surface preparation processes requiring particularly low roughness, flexible abrasives with polyester film support can also be used, with grits up to 0.5µ/>P5000.
---EDITOR: Doris Hu
---POST: Doris Hu
Semiconductor Industry Solutions
PCD & PCBN Tools Grinding Industry
Diamond Cutting Bruting Polishing
Add: No.171 Zhongyuan Rd, Zhongyuan District, Zhengzhou, 450001, Henan, China
Tel: +86-371-86545906
Phone / Whats App: +86 18339903057
E-mail: [email protected]



